Navigation
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Nahitaji msaada/mawazo ya kitabibu wakuu!
- Thread starter iNine9
- Start date
iNine9
JF-Expert Member
- Mar 1, 2017
- 4,231
- 7,815
- Thread starter
- #25
Shukrani sana mkuu vp lakini zinaweza saidia hiyo hali kuacha? Sabu hii week niliugua tumbo vibaya sana ni mpaka nililazwa na kupigwa drip 6 ndo nikapata fahamu..Times9
Hiyo condition walotaja hapo ni kufura kwa kidney hivyo Basi kuna shida nyengine inayo sababisha huko kufura.
Pengine ni UTI etc hivyo Basi ni muhimu umalize hiyo dose na utumie maji safi mengi sana.
Rgds
Alafu kila nimalizao kutumia hizi dawa nahisi kama tumbo linawaka moto sana kushoto pembeni mwa kitovu inaweza kua ni side effects za dawa au..? Naona ni new condition kabisa hii before haikua hivo..
iNine9
JF-Expert Member
- Mar 1, 2017
- 4,231
- 7,815
- Thread starter
- #26
Radiology-Main 2021-01-22 1434Kwa historia ya zamani ya kujikojolea na hii ya sasa ya kukojoa mara kwa mara , na kama kuna muda unapata hamu ya kukojoa ila ukienda unapata mkono kidogo tu unaweza kua na tatizo linaitwa "Overactive bladder syndrome" ambalo hutokana na shida ya mfumo wa fahamu unaosupply kibofu kuruhusu kubana na kuachia mkojo , matibabu yake yapo kwa dawa na mazoezi angalau kwa miezi mitatu na kuendelea , Kuna dawa nzuri sana inaitwa Oxybutynin ukifanya na mazoezi ya pelvic floor muscles utapata matokeo mazuri sana.
Onana na urologist alie karibu na wewe akupe mpangilio mzuri wa matibabu.
GENERAL USS Abdomen + Pelvic
2021-01-22 15:06
Report: ABDOMINO-PELVIC ULTRASOUND
Urinary bladder appear well distended. Bladder wall is thick and is irregular
Kidneys appear normal in size. Pevicalycenl systems are mildly enlarged in rt kidney. Preserved corticomedullary differentiaton: No stone no
mas no cyst seen
Liver, splieen and pancreas appear normal
Other findings normal
IMPRESSION, Features are suggestive to: Cystilis
Rt caliectasis
Hii baada ya kufanya ULTRASOUND mkuu ndo majibu yaliyopatikana..
iNine9
JF-Expert Member
- Mar 1, 2017
- 4,231
- 7,815
- Thread starter
- #27
Radiology-Main 2021-01-22 1434Mkuu Pole na maradhi yako na mimi nina changia kama walivyo changia wenzangu kuwa unatakiwa ukapime maradhi ya aiana 3 ya njia ya mkojo Maradhi yenyewe ni overactive bladder, au Enlarged Prostate, au Urinary incontinence Hiyo ya mwisho aka Urinary incontinence yaani unakojoa wakati hutaki hata kukojoa kutokana na udhaifu wakibofu chako cha mkojo kutozuia mkojo wako. Na uangalie tena katika figo lako je hayo maambukzi yamekwisha?Ingawa huja tuambia wewe ni mwanamke au Mwanamume?
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life.[1] It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care.[2] The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting).[3]
Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major risk factors.[4] Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners.[5] There are four main types of incontinence:[6]
Treatments include pelvic floor muscle training, bladder training, surgery, and electrical stimulation.[8] Behavioral therapy generally works better than medication for stress and urge incontinence.[9] The benefit of medications is small and long term safety is unclear.[8] Urinary incontinence is more common in older women.[10]
- Urge incontinence due to an overactive bladder
- Stress incontinence due "a poorly functioning urethral sphincter muscle (intrinsic sphincter deficiency) or to hypermobility of the bladder neck or urethra"[7]
- Overflow incontinence due to either poor bladder contraction or blockage of the urethra
- Mixed incontinence involve features of different other types
Causes
Urinary incontinence can result from both urologic and non-urologic causes. Urologic causes can be classified as either bladder dysfunction or urethral sphincter incompetence and may include detrusor overactivity, poor bladder compliance, urethral hypermobility, or intrinsic sphincter deficiency. Non-urologic causes may include infection, medication or drugs, psychological factors, polyuria, stool impaction, and restricted mobility.[11] The causes leading to urinary incontinence are usually specific to each sex, however, some causes are common to both men and women.
Women

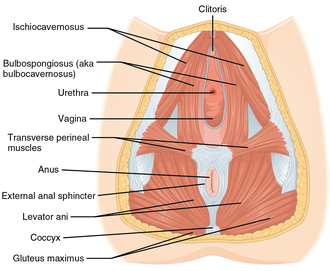
Pelvic floor muscles in women
The most common types of urinary incontinence in women are stress urinary incontinence and urge urinary incontinence. Women that have symptoms from both types are said to have "mixed" urinary incontinence. After menopause, estrogen production decreases and, in some women, urethral tissue will demonstrate atrophy, becoming weaker and thinner, possibly playing a role in the development of urinary incontinence.[4]
Stress urinary incontinence in women is most commonly caused by loss of support of the urethra, which is usually a consequence of damage to pelvic support structures as a result of pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, age, among others.[12] About 33% of all women experience urinary incontinence after giving birth, and women who deliver vaginally are about twice as likely to have urinary incontinence as women who give birth via a Caesarean section.[13] Stress incontinence is characterized by leaking of small amounts of urine with activities that increase abdominal pressure such as coughing, sneezing, laughing and lifting. This happens when the urethral sphincter cannot close completely due to the damage in the sphincter itself, or the surrounding tissue. Additionally, frequent exercise in high-impact activities can cause athletic incontinence to develop. Urge urinary incontinence, is caused by uninhibited contractions of the detrusor muscle, a condition known as overactive bladder syndrome. It is characterized by leaking of large amounts of urine in association with insufficient warning to get to the bathroom in time.
Men

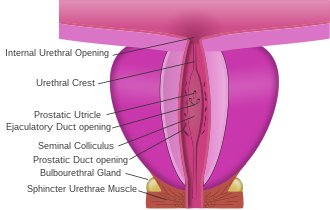
The prostate with the urethra passing through it (prostatic urethra)
Urge incontinence is the most common type of incontinence in men.[14] Similar to women, urine leakage happens following a very intense feeling of urination, not allowing enough time to reach the bathroom, a condition called overactive bladder syndrome. In men, the condition is commonly associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (an enlarged prostate), which causes bladder outlet obstruction, a dysfunction of the detrusor muscle (muscle of the bladder), eventually causing overactive bladder syndrome, and the associated incontinence.[14]
Stress urinary incontinence is the other common type of incontinence in men, and it most commonly happens after prostate surgery.[15] Prostatectomy, transurethral resection of the prostate, prostate brachytherapy, and radiotherapy can all damage the urethral sphincter and surrounding tissue, causing it to be incompetent. An incompetent urethral sphincter cannot prevent the urine from leaking out of the urinary bladder during activities that increase the intraabdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing. Continence usually improves within 6 to 12 months after prostate surgery without any specific interventions, and only 5 to 10% of people report persistent symptoms.[14]
Both
- Age is a risk factor that increases both the severity and prevalence of UI
- Polyuria (excessive urine production) of which, in turn, the most frequent causes are: uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, primary polydipsia (excessive fluid drinking), central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.[16] Polyuria generally causes urinary urgency and frequency, but does not necessarily lead to incontinence.
- Neurogenic disorders like multiple sclerosis, spina bifida, Parkinson's disease, strokes and spinal cord injury can all interfere with nerve function of the bladder.[17] This can lead to neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- Overactive bladder syndrome. However, the etiology behind this is usually different between men and women, as mentioned above.
- Other suggested risk factors include smoking, caffeine intake and depression
Mechanism

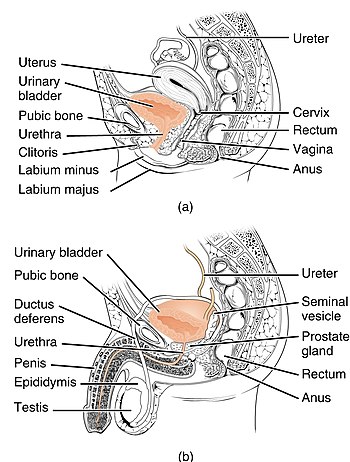
Anatomy of the lower urinary tract and genital system
Adults
The body stores urine — water and wastes removed by the kidneys — in the urinary bladder, a balloon-like organ. The bladder connects to the urethra, the tube through which urine leaves the body.
Continence and micturition involve a balance between urethral closure and detrusor muscle activity (the muscle of the bladder). During urination, detrusor muscles in the wall of the bladder contract, forcing urine out of the bladder and into the urethra. At the same time, sphincter muscles surrounding the urethra relax, letting urine pass out of the body. The urethral sphincter is the muscular ring that closes the outlet of the urinary bladder preventing urine to pass outside the body. Urethral pressure normally exceeds bladder pressure, resulting in urine remaining in the bladder, and maintaining continence.[18] The urethra is supported by pelvic floor muscles and tissue, allowing it to close firmly. Any damage to this balance between the detrusor muscle, urethral sphincter, supportive tissue and nerves can lead to some type of incontinence .
For example, stress urinary incontinence is usually a result of the incompetent closure of the urethral sphincter. This can be caused by damage to the sphincter itself, the muscles that support it, or nerves that supply it. In men, the damage usually happens after prostate surgery or radiation,[14] and in women, it's usually caused by childbirth and pregnancy.[19] The pressure inside the abdomen (from coughing and sneezing) is normally transmitted to both urethra and bladder equally, leaving the pressure difference unchanged, resulting in continence. When the sphincter is incompetent, this increase in pressure will push the urine against it, leading to incontinence.
Another example is urge incontinence. This incontinence is associated with sudden forceful contractions of the detrusor muscle (bladder muscle), leading to an intense feeling of urination, and incontinence if the person does not reach the bathroom on time. The syndrome is known as overactive bladder syndrome, and it's related to dysfunction of the detrusor muscle.[20]
GENERAL USS Abdomen + Pelvic
2021-01-22 15:06
Report: ABDOMINO-PELVIC ULTRASOUND
Urinary bladder appear well distended. Bladder wall is thick and is irregular
Kidneys appear normal in size. Pevicalycenl systems are mildly enlarged in rt kidney. Preserved corticomedullary differentiaton: No stone no
mas no cyst seen
Liver, splieen and pancreas appear normal
Other findings normal
IMPRESSION, Features are suggestive to: Cystilis
Rt caliectasis
Hiki ndo kilichoonekana baada vipimo mkuu..
MzeeMpya
JF-Expert Member
- Dec 19, 2019
- 513
- 654
Pole na maradhi. Nadhani wataalamu wengi wamechangia huu uzi. Tatizo lako linasababishwa na mifumo ya fahamu kutofanya mawasiliano ipasavyo baina ya figo kidney na kibofu cha mkojo. Nakushauri uanze kutumia hii tiba mbadala nyepesi. Unaweza kuytumia hata kama unatumia dawa za hospital. Lengo ni kuuengeza nguvu na vichecheo ndani ya michipa yako ya fahamu kwenda mifumo mengine ilioathirika.
Tumia Asali mbichi au Asali wa nyuki wa dogo na mdalasini wa unga. Tengeneza kwa mfumo wa chakula. Hakikisha kwa siku unakula ujazo wa kikombe cha chai.
ANGALIZO MUHIMU.
Hakikisha unapima kiwango chako cha sukari mara kwa mara.
Kama ww ni mwislam wa swala tanu. Unitafute nikupe URADI utakao weza kukupa njia ya haraka ndani ya matibabu yako.
Wabillah Taufiq....
Tumia Asali mbichi au Asali wa nyuki wa dogo na mdalasini wa unga. Tengeneza kwa mfumo wa chakula. Hakikisha kwa siku unakula ujazo wa kikombe cha chai.
ANGALIZO MUHIMU.
Hakikisha unapima kiwango chako cha sukari mara kwa mara.
Kama ww ni mwislam wa swala tanu. Unitafute nikupe URADI utakao weza kukupa njia ya haraka ndani ya matibabu yako.
Wabillah Taufiq....
COMOTANG
JF-Expert Member
- Jan 6, 2021
- 2,131
- 1,808
Mkuu
Ipo chai ambayo itakuondolea adha hiyo.NITUMIE NAMBA YAKO YA WASAP NIKUTUMIE VIFAA VYA HIYO CHAI UITENGENEZE MWENYEWE KWA VIFAA VYA ASILIWasalaam wakuu..
Bila kupoteza muda niende moja moja kuelezea tatizo linanonisibu, Mimi ni kijana wa Kiume kwa muda mrefu sasa nmekua na tatizo ambalo nimeshindwa kuelewa kabisa sababu ni nini au ni kawaida tu?
Iko hivi kila nimalizapo kujisaidia haja ndogo nmekua nikipata mshtuko flani hivi ni kama nmepigwa shoti ya umeme au nmeshtuliwa na kitu cha kuogofya kwa ghafla sana...., Hii hali hainitokei kila nikojoapo lakini huwa inatokea sana miaka mingi sasa nina shida hii, Nilishajaribu kuwauliza madaktari lakini hakuna hata mmoja alieniambia tatizo ni nini zaidi kuishia kupimwa UTI, Kisukari & figo (Kwenye figo nishawahi kukutwa na maambukizi ila nilipatiwa dawa za kutibu) but hali ya mshtuko baada ya kukojoa still ipo...
Kingine wakuu sambamba na hilo tatizo, ni kua ninahisi kukojoa kojoa kila mara hasa wakati nikinywa kinywaji chochote(N.B Situmii vilevi), vyakula/matunda yenye maji maji basi natakiwa nisiwe mbali na eneo la kujisaidia haja ndogo kila mara, yaani kama vile huwa nakunywa vinywaji, iwe maji, soda, tikiti maji basi yale maji yanapitiliza tu bila hata kufanyiwa absorption mwilini hii ni nyakati zozote, iwe wakati wa joto au mazingira ya baridi nitakojoa sana mpaka sio poa up to now nina hili tatizo!
Early nishawahi pia kua na tatizo la ukojozi kwa muda wa miaka 10+ nilitumia madawa yote unayoyajua ww ya kuzuia au kutibu hilo tatizo ya hospital & antibiotics but hazikusaidiaga kitu! Ila nilikujaga pona nikiwa na 20 yrs kwa uwezo wake Allah kwa hakika niliteseka/dharirika sana na hali hii basi tu sitakagi hata kumbuka kabisa zaidi ya kumshukuru Mwenyezi Mungu nilipona bila dawa!
Matatizo yaliyobaki ni hayo kupata mshtuko na swala la kukojoa mara kwa mara, kuna muda naogopaga kunywa hata maji wakuu hasa nikijua naenda mishe mishe za ubize sana au nasafiri inabidi niache tumia kinywaji kabisa...
.....Msaada wenu wakuu wa mawazo na tiba juu ya haya masaibu, natanguliza shukrani!
Mrejesho
Radiology-Main 2021-01-22 1434
GENERAL USS Abdomen + Pelvic
2021-01-22 15:06
Report: ABDOMINO-PELVIC ULTRASOUND
Urinary bladder appear well distended. Bladder wall is thick and is irregular
Kidneys appear normal in size. Pevicalycenl systems are mildly enlarged in rt kidney. Preserved corticomedullary differentiaton: No stone no
mas no cyst seen
Liver, splieen and pancreas appear normal
Other findings normal
IMPRESSION, Features are suggestive to: Cystilis
Rt caliectasis
Similar Discussions
-
Uzi maalumu wa Mimea Tiba inayotuzunguka majumbani
- Started by Crocodiletooth
- Replies: 2K
-
Swali kwa Kamati ya Dira ya Taifa: "Umoja wa Taifa ni Chachu ya Maendeleo au Maendeleo ni Chachu ya Umoja wa Taifa?"
- Started by Mama Amon
- Replies: 7
-
Teaching the ten sexes in humans as an antidote to patriarchy: Why did we forget this for half a century?
- Started by Mama Amon
- Replies: 1
-